Rotating 3D Objects
This section covers how to rotate 3D objects.
Rotating Models
For continuously rotating models (e.g. during animation), it is generally best to use coordinate systems, which will be discussed in a later chapter.
However, if you just want to rotate a model once, you can easily do so using functions like rotModel introduced in this section.
Unlike translation, multiple rotation functions are available. Use the appropriate one depending on your use case.
Rotation Around Coordinate Axes
To rotate a model around one of the coordinate axes, use the rotXModel, rotYModel, or rotZModel function.
- Function Format -
void rotXModel ( int modelID, float angle )
void rotYModel ( int modelID, float angle )
void rotZModel ( int modelID, float angle )
These three functions rotate the model around the X-, Y-, and Z-axis respectively.
Arguments:
- modelID: Specifies the ID of the model to rotate.
- angle: Specifies the rotation angle in radians. The positive direction follows the right-hand rule based on the axis orientation.
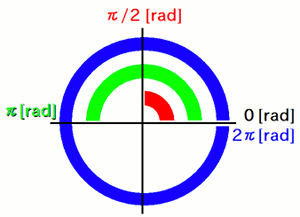
What is a radian?
A radian is a unit of angle frequently used in science and engineering.
One full half-turn (180 degrees) is equal to π radians, so 90 degrees is π/2 radians, and 45 degrees is π/4 radians.
The value of π is provided as the float constant "PI" in the Math library.
Rotation Around an Arbitrary Direction Vector
To rotate around an axis in an arbitrary direction, use the rotModel(...) function.
- Function Format -
void rotModel (
int modelID,
float angle,
float vx, float vy, float vz
)
Arguments:
- modelID: Specifies the ID of the model to rotate.
- angle: Specifies the rotation angle in radians. The positive direction follows the right-hand rule.
- vx, vy, vz: Specify the components of the direction vector for the rotation axis.
Rotation Around a Vector with Arbitrary Origin and Direction
To rotate around an axis that passes through a specific point and has an arbitrary direction, use the extended version of the rotModel(...) function.
- Function Format -
void rotModel (
int modelID,
float angle,
float vx, float vy, float vz,
float px, float py, float pz
)
Arguments:
- modelID: Specifies the ID of the model to rotate.
- angle: Specifies the rotation angle in radians. The positive direction follows the right-hand rule.
- vx, vy, vz: Specify the components of the direction vector for the rotation axis.
- px, py, pz: Specify the coordinates of the point through which the rotation axis passes.
Rotating Polygons
Just like with models, multiple functions are available for rotating individual polygons.
Rotation Around Coordinate Axes
To rotate a polygon around one of the coordinate axes, use the rotXPolygon(...), rotYPolygon(...), or rotZPolygon(...) function.
- Function Format -
void rotXPolygon ( int polygonID, float angle )
void rotYPolygon ( int polygonID, float angle )
void rotZPolygon ( int polygonID, float angle )
These three functions rotate the polygon around the X-, Y-, and Z-axis respectively.
Arguments:
- polygonID: Specifies the ID of the polygon to rotate.
- angle: Specifies the rotation angle in radians. The positive direction follows the right-hand rule.
Rotation Around an Arbitrary Direction Vector
To rotate around an axis in an arbitrary direction, use the rotPolygon(...) function.
- Function Format -
void rotPolygon (
int polygonID,
float angle,
float vx, float vy, float vz
)
Arguments:
- polygonID: Specifies the ID of the polygon to rotate.
- angle: Specifies the rotation angle in radians. The positive direction follows the right-hand rule.
- vx, vy, vz: Specify the components of the direction vector for the rotation axis.
Rotation Around a Vector with Arbitrary Origin and Direction
To rotate around an axis that passes through a specific point and has an arbitrary direction, use the extended version of the rotPolygon(...) function.
- Function Format -
void rotPolygon (
int polygonID,
float angle,
float vx, float vy, float vz,
float px, float py, float pz
)
Arguments:
- polygonID: Specifies the ID of the polygon to rotate.
- angle: Specifies the rotation angle in radians. The positive direction follows the right-hand rule.
- vx, vy, vz: Specify the components of the direction vector for the rotation axis.
- px, py, pz: Specify the coordinates of the point through which the rotation axis passes.
Example Programs
Basic Example: Rotating a Model Once
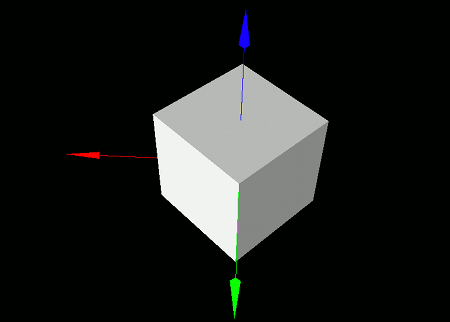
Let's try placing a box-shaped model and rotating it 45 degrees (π/4 radians) around the Z-axis.
Write and run the following code:
import graphics3d.Graphics3DFramework;
import Graphics3D;
import Math; // For the value of PI
// Function called at the start of the program
void onStart ( int rendererID ) {
// Optional: Set window size and background color
setWindowSize( 800, 600 );
setBackgroundColor( 0, 0, 0, 255 );
// Create and place an axis model
int axis = newAxisModel( 3.0, 3.0, 3.0 );
mountModel( axis, rendererID );
// Create and place a box-shaped model
int box = newBoxModel( 2.0, 2.0, 2.0 );
mountModel( box, rendererID );
// Rotate the box 45 degrees (pi/4 radians) around the Z-axis
rotModelZ( box, PI/4.0 );
}
Rot.vcssl
When you run this program, a white box will appear on a black background.
The box is rotated 45 degrees (π/4 radians) around the Z-axis.
Animated Rotation Example
To rotate a model continuously in an animation, you can use the onUpdate(...) function, which is automatically called several dozen times per second by the framework:
import graphics3d.Graphics3DFramework;
import Graphics3D;
import Math; // For the value of PI
// Variables to store the model IDs
int axis, box;
// Function called at the start of the program
void onStart ( int rendererID ) {
// Optional: Set window size and background color
setWindowSize( 800, 600 );
setBackgroundColor( 0, 0, 0, 255 );
// Create and place an axis model
axis = newAxisModel( 3.0, 3.0, 3.0 );
mountModel( axis, rendererID );
// Create and place a box-shaped model
box = newBoxModel( 2.0, 2.0, 2.0 );
mountModel( box, rendererID );
}
// Function called several dozen times per second during each frame update
void onUpdate (int renderer) {
// Gradually rotate the box around the Z-axis
rotModelZ( box, 0.02 );
}
RotAnimation.vcssl
When you run this program, the white box will slowly and continuously rotate like an animation.
Author of This Article
Fumihiro Matsui
[ Founder of RINEARN, Doctor of Science (Physics), Applied Info Tech Engineer ]
Develops VCSSL, RINEARN Graph 3D and more. Also writes guides and articles.
Translation Cooperator
ChatGPT AIs
[ GPT-3.5, 4, 5, 5.1 ]
We greatly appreciate the cooperation of ChatGPT AIs in translating this article.