This section covers how to flip models and polygons. In VCSSL, there are two types of flipping operations for 3D objects:
The surfaces of a model have a front and a back side.
Surfaces are rendered only when viewed from the front; the back sides are invisible. For standard models, the outer surfaces are typically the front side, so nothing is visible from the inside.
However, in applications such as game development, there are many cases where you want the inner side of a model to be visible -- for example, when creating a sky dome or a tunnel-like corridor. In such cases, you can use reverse flipping to invert the front and back sides of the model.
To perform reverse flipping on a model, use the reverseModel function.
- Function Format -
Argument:
Like models, triangle and quadrilateral polygons also have a front and back side. To reverse-flip a polygon, use the reversePolygon(...) function.
- Function Format -
Argument:
If you want to flip a model symmetrically, for example across the X-axis, you can perform a mirror flip using the mirrorModel(...) function.
- Function Format -
Arguments:
To mirror-flip a polygon, use the mirrorPolygon(...) function.
- Function Format -
Arguments:
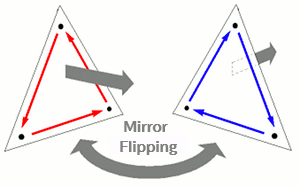
There's an important point to keep in mind: Performing a mirror flip also inverts the front/back orientation of surfaces.
This occurs because a clockwise vertex order becomes counterclockwise after mirroring (and vice versa). In VCSSL, the front side of a surface is determined by whether the polygon's vertices are arranged in counterclockwise order.
When you apply a mirror flip, this order is reversed -- so what was the front side becomes the back side after the flip.
Therefore, every time you mirror-flip a model or polygon, you should also call "reverseModel" or "reversePolygon" to correct the surface orientation.

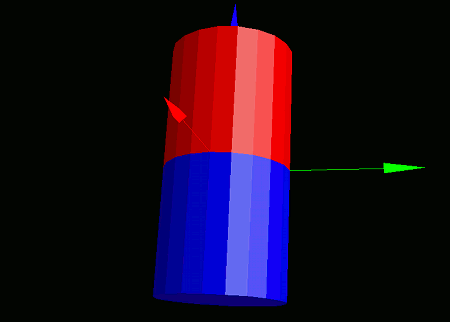
Let's place a cylinder model and apply a mirror flip along the Z direction. Because mirror flipping also reverses the surface orientation, we correct it using reverse flipping. Write and run the following code:
import graphics3d.Graphics3DFramework;
import Graphics3D;
// Function called at the start of the program
void onStart ( int rendererID ) {
// Optional: Set window size and background color
setWindowSize( 800, 600 );
setBackgroundColor( 0, 0, 0, 255 );
// Create and place axis model
int axis = newAxisModel( 3.0, 3.0, 3.0 );
mountModel( axis, rendererID );
// Create and place first cylinder
int cylinder1 = newCylinderModel( 1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 20, 1 );
setModelColor( cylinder1, 255, 0, 0, 255 ); // red
mountModel( cylinder1, rendererID );
// Create and place second cylinder
int cylinder2 = newCylinderModel( 1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 20, 1 );
setModelColor( cylinder2, 0, 0, 255, 255 ); // blue
mountModel( cylinder2, rendererID );
// Mirror-flip the second cylinder in the Z direction
mirrorModel( cylinder2, false, false, true );
reverseModel( cylinder2 ); // correct surface orientation
}
When you run this program, two cylinders will appear on a black background: one red and one blue. The blue cylinder is a mirror-flipped version of the red one along the Z-axis.