This section explains how to configure material properties for 3D objects. Here, "material" does not refer to surface patterns or textures, but rather to characteristics related to how the object reflects light.
In the real world, the appearance of an object varies depending on its material. For example, a flat board will look "dry" if it's made of paper, but will look "shiny" if it's made of plastic. There are several reasons for these differences, but arguably the most significant factor is how the object reflects light.
Light reflection can be broken down into several components.
Take a plastic board, for instance. The surface appears uniformly lit because light hits the plastic and diffusely reflects in many directions, some of which reach our eyes. Meanwhile, the sharp, bright spots (highlights) are caused by specular reflection -- light rays bouncing directly off the surface. As for the areas in shadow, they are often faintly illuminated by scattered light that has bounced through the surrounding air and reached the back side of the object.
3DCG expresses different materials by adjusting the balance of these types of reflections. These adjustable balances are called material parameters.
Let's go through each of the major material parameters.
The diffuse reflection parameter controls how much incoming light is diffusely reflected in various directions -- like how light scatters off a sheet of paper.
This parameter significantly affects the perceived "dryness" or "matteness" of a surface. If you want to render materials like cloth or paper, increase this value. For metal-like surfaces, keep it lower.

To set the diffuse reflection parameter for a model, use the setModelDiffuse(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
To set the diffuse reflection parameter for a polygon, use the setPolygonDiffuse(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
The diffractive reflection parameter controls how much light is scattered in the air around the object and curves around to illuminate the back side. Without this effect, the back sides of objects appear pitch-black, like celestial bodies in space.
This parameter behaves similarly to the ambient reflection parameter discussed later, but differs in that diffractive reflection creates a gradient depending on the angle of the light source.
To set the diffractive reflection parameter for a model, use the setModelDiffractive function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
To set the diffractive reflection parameter for a polygon, use the setPolygonDiffractive(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
The ambient reflection parameter adjusts the effect of ambient light -- that is, light coming uniformly from the surrounding environment. In reality, light doesn't always travel in straight lines directly from a light source. Some of it reflects off walls or other surfaces and then indirectly illuminates the object. This surrounding light is called ambient light.
This parameter is used similarly to the diffractive reflection parameter. However, ambient reflection differs in that it has no directional dependency, resulting in a uniform illumination across the entire object.
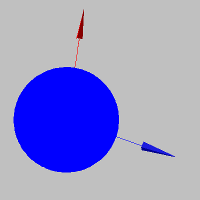
To apply the ambient reflection parameter to a model, use the setModelAmbient(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
To apply the ambient reflection parameter to a polygon, use the setPolygonAmbient(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
The specular reflection parameter controls how much incoming light reflects directly off the surface without scattering. This simulates mirror-like highlights often seen on smooth surfaces such as plastic.
By adjusting this parameter, you can control how shiny or glossy a surface appears.
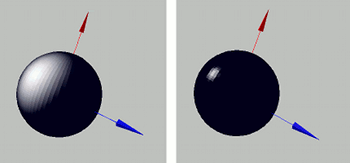
To apply the specular reflection parameter to a model, use the setModelSpecular(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
To apply the specular reflection parameter to a polygon, use the setPolygonSpecular(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
The emissive parameter controls how strongly an object appears to emit light uniformly from its surface. Its visual effect is similar to ambient reflection, but it remains completely unaffected by the brightness of any light sources.
To apply the emissive parameter to a model, use the setModelEmissive(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:
To apply the emissive parameter to a polygon, use the setPolygonEmissive(...) function:
- Function Format -
Arguments:

