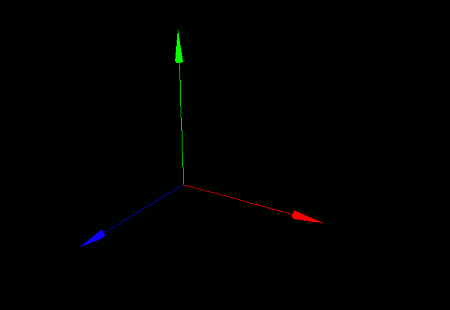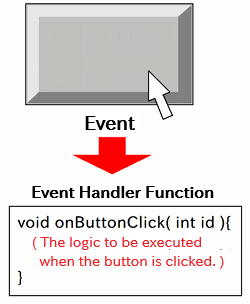
Since 3D graphics involve working with solid objects, the image you see changes depending on the viewing angle (camera angle).
It's very useful to be able to adjust the viewpoint using mouse controls. This section explains how to implement such functionality.
We won't go into full detail here, but when a user performs actions -- like mouse operations -- on a GUI component, a special function called an event handler is automatically called by the system. For more details, please refer to the GUI Library Guide.

For example, if you want to change the camera angle based on mouse input, you'll need to set up a mouse event handler.
There are two approaches:
In this guide, we'll use the first approach -- the built-in handler.
- Function Format -
Arguments:
To perform animation, your program must keep redrawing the screen continuously from the moment it starts until it ends. In other words, you need a control flow that resembles an infinite loop.
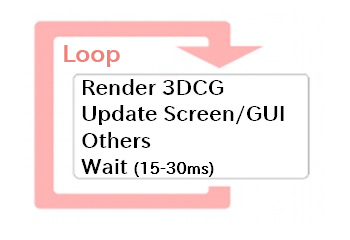
bool mainLoopState = true; // Set to false when you want to exit the animation
while( mainLoopState ){
/* This is the main animation loop: write rendering logic here */
}
If you use an infinite loop like the one above, you need to make sure the program can automatically exit when the window is closed. Otherwise, especially in cases where the VCSSL console is hidden or not available, there would be no way to stop the program -- it would keep animating forever.
To handle this, define an event handler named "onWindowClose", which will be called automatically when the window is closed:
- Function Format -
The "componentID" parameter receives the ID of the GUI component (the window) that was closed.
When you define this function, the system will call it automatically when the window is closed.
Now let's write an actual animation program.
To make camera movement easier to understand, we'll add an axis model to the scene. We'll cover model generation and placement in detail in the next section, but for now, just copy and run the following:
import Graphics;
import Graphics3D;
import GUI;
// Create graphics resource and 3D renderer
int graphicsID = newGraphics( );
int rendererID = newGraphics3DRenderer( 800, 600, graphicsID );
// Create display window
int windowID = newWindow( 0, 0, 800, 600, " Hello 3DCG ! " );
int labelID = newImageLabel( 0, 0, 800, 600, graphicsID );
mountComponent( labelID, windowID );
// Enable mouse-based camera control
setGraphics3DDefaultEventHandler( rendererID, labelID );
// Set background color to black
setGraphics3DColor( rendererID, 0, 0, 0, 255 );
// Generate and place the axis model
int axis = newAxisModel( 3.0, 3.0, 3.0 );
mountModel( axis, rendererID );
// Animation loop
bool mainLoopState = true;
while( mainLoopState ) {
sleep( 30 ); // Wait for 30 milliseconds
paintGraphics3D( rendererID ); // Render 3DCG
paintComponent( labelID ); // Refresh GUI
paintComponent( windowID ); // Refresh GUI
}
exit(); // Exit program after breaking the loop
// Called when the window is closed
void onWindowClose( int id ) {
mainLoopState = false; // Exit the loop
}
When you run this program, a window will appear showing a coordinate axis model against a black background.