Now that you're all set up to use 2DCG, it's time to start drawing.
As your first step, let's look at how to clear the drawing area and set the background color.
To clear the contents of a graphics resource that already has something drawn on it, use the "clearGraphics2D" function.
- Function Format -Arguments:
When you call this function, the renderer will clear the contents of the associated graphics resource, filling it entirely with the background color.
By default, the background color is transparent, which means the base layer of the window will show through.
Depending on your environment, this base layer may appear white, gray, or some other color. So if you plan to display the graphics resource in a window, it's recommended to set the background to an opaque color in advance.
You can set the background color using the function explained below.
To set the background color, use the "setGraphics2DColor" function.
- Function Format -Arguments:
RGBA stands for Red, Green, Blue, and Alpha -- the three primary colors of light, plus an alpha value that represents transparency.
The alpha value controls how transparent the color is: 0 means fully transparent, and higher values move toward full opacity.
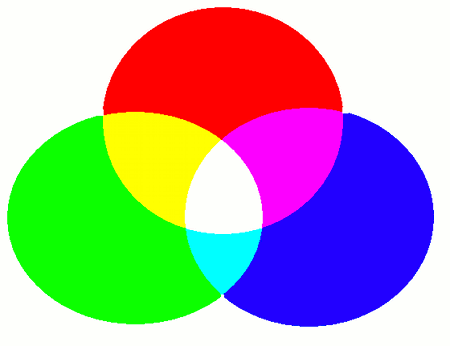
The color is produced using additive color mixing, which is the same principle as how light is blended -- not like mixing paints (which uses subtractive color mixing). For example:

Let's try setting the background color to blue. Write and run the following code:
import Graphics;
import Graphics2D;
import GUI;
// Create a graphics resource and a renderer
int graphicsID = newGraphics( );
int rendererID = newGraphics2DRenderer( 800, 600, graphicsID );
// Create a display window
int windowID = newWindow( 0, 0, 800, 600, " Hello 2DCG ! " );
int labelID = newImageLabel( 0, 0, 800, 600, graphicsID );
mountComponent( labelID, windowID );
// Set the background color to blue
setGraphics2DColor( rendererID, 0, 0, 255, 255 );
// Clear the graphics using the background color
clearGraphics2D( rendererID );
// Paint the GUI components
paintComponent( labelID );
paintComponent( windowID );
When you run this program, a window filled with a solid blue color will appear on the screen.


